简介
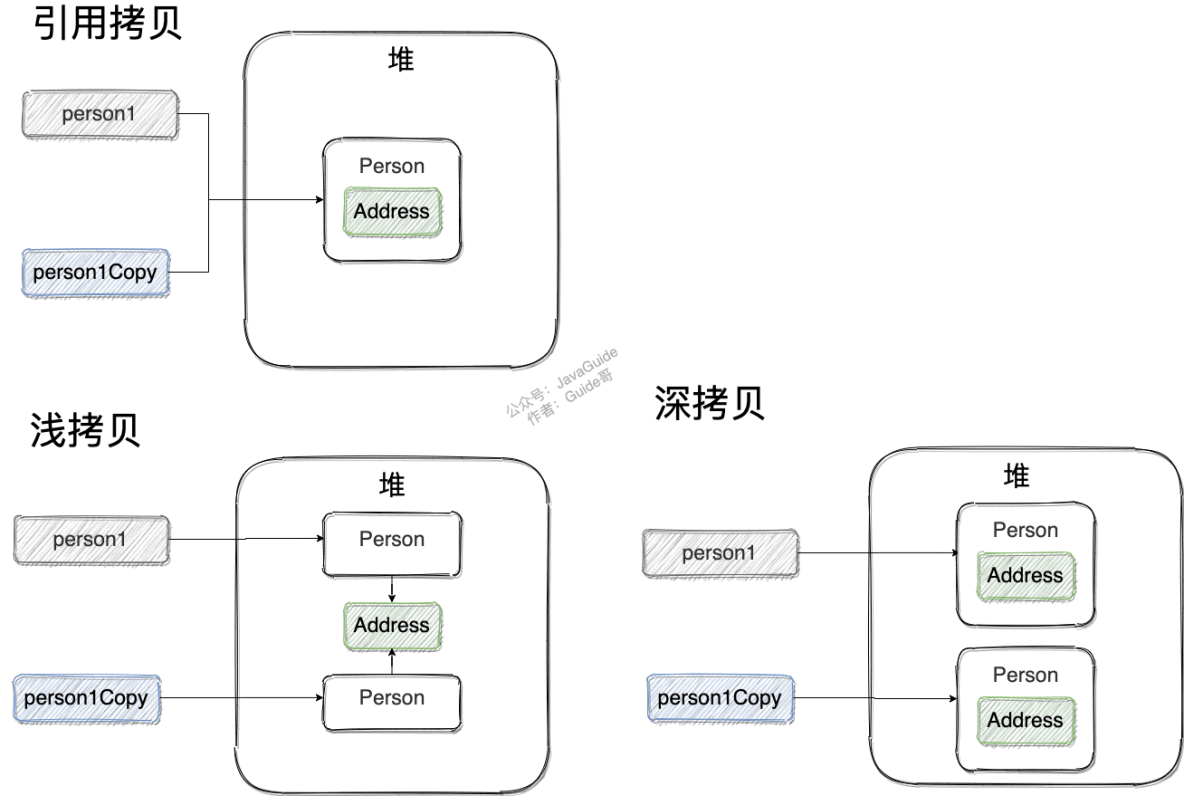
- 浅拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值的传递,对引用数据类型进行引用传递的拷贝。
- 深拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型,创建一个新的对象,并复制其内容。
浅拷贝
我们创建一个Parent类和Child类为例,实现浅拷贝只需要让Parent继承Cloneable接口,并且重写clone()方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class Parent implements Cloneable {
String parentName;
Child child;
public Parent(String parentName, Child child) {
this.parentName = parentName;
this.child = child;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class Child {
String childName;
public Child(String childName) {
this.childName = childName;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Parent parent1 = new Parent("parent name", new Child("child name"));
Parent parent2 = (Parent) parent1.clone();
System.out.println(parent1 == parent2);
System.out.println("parent1: " + parent1.hashCode());
System.out.println("parent2: " + parent2.hashCode());
System.out.println("==============");
System.out.println(parent1.child == parent2.child);
System.out.println("child1: " + parent1.child.hashCode());
System.out.println("child2: " + parent2.child.hashCode());
System.out.println(parent1.child.childName);
System.out.println(parent2.child.childName);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| false
parent1: 1456208737
parent2: 25126016
parent name
parent name
==============
true
child1: 762218386
child2: 762218386
child name
child name
|
通过哈希值和==操作服可以发现,浅拷贝确实创建了一个新的对象。但是对于引用类型的属性child而言,从哈希值可以发现浅拷贝过后仍然引用了相同的Child对象,即浅拷贝只传递了属性为引用类型的引用。
深拷贝
常用实现深拷贝的方案有两种:
- 序列化这个对象,再反序列化回来,就可以得到这个新的对象。
- 继续利用
clone()方法,但是属性中的引用对象也要实现Cloneable接口并重写clone()方法。
改变属性中的引用对象
和之前的浅拷贝不同之处在于Child也实现了Cloneable,并重写了clone()方法,而Parent的clone()方法也有略微不同,在调用了clone()方法后还调用了属性child的clone()方法重新设置属性,实现完全的拷贝。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class Parent implements Cloneable {
String parentName;
Child child;
public Parent(String parentName, Child child) {
this.parentName = parentName;
this.child = child;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Parent parentclone = (Parent) super.clone();
parentclone.child = (Child) this.child.clone();
return parentclone;
}
}
public class Child implements Cloneable {
String childName;
public Child(String childName) {
this.childName = childName;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| false
parent1: 1456208737
parent2: 25126016
parent name
parent name
==============
false
child1: 762218386
child2: 672320506
child name
child name
|
通过哈希值可以发现,原始对象和拷贝对象的属性child已经是两个不同的对象。
序列化
如果使用序列化,那么两个类都不需要再实现Cloneable接口并重写clone()方法,但是它们都需要实现Serializable接口,并且在Parent的克隆方法中要实现序列化反序列化的逻辑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Parent implements Serializable {
String parentName;
Child child;
public Parent(String parentName, Child child) {
this.parentName = parentName;
this.child = child;
}
public Object deepClone() throws Exception {
OutputStream bo = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oo = new ObjectOutputStream(bo);
oo.writeObject(this);
InputStream bi = new ByteArrayInputStream(((ByteArrayOutputStream) bo).toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream oi = new ObjectInputStream(bi);
return oi.readObject();
}
}
public class Child implements Serializable {
String childName;
public Child(String childName) {
this.childName = childName;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| false
parent name
parent name
==================
false
child name
child name
|
引用拷贝
除了深拷贝和浅拷贝之外还有引用拷贝,它指的是两个不同的引用指向同一个对象。
参考
- Java中的深拷贝与浅拷贝-水木今山的博客
- 细说 Java 的深拷贝和浅拷贝
- 菜鸟教程-ByteArrayOutputStream类
- JavaGuide
